The Vagus Nerve’s Crucial Role in Creating the Human Sense of Mind
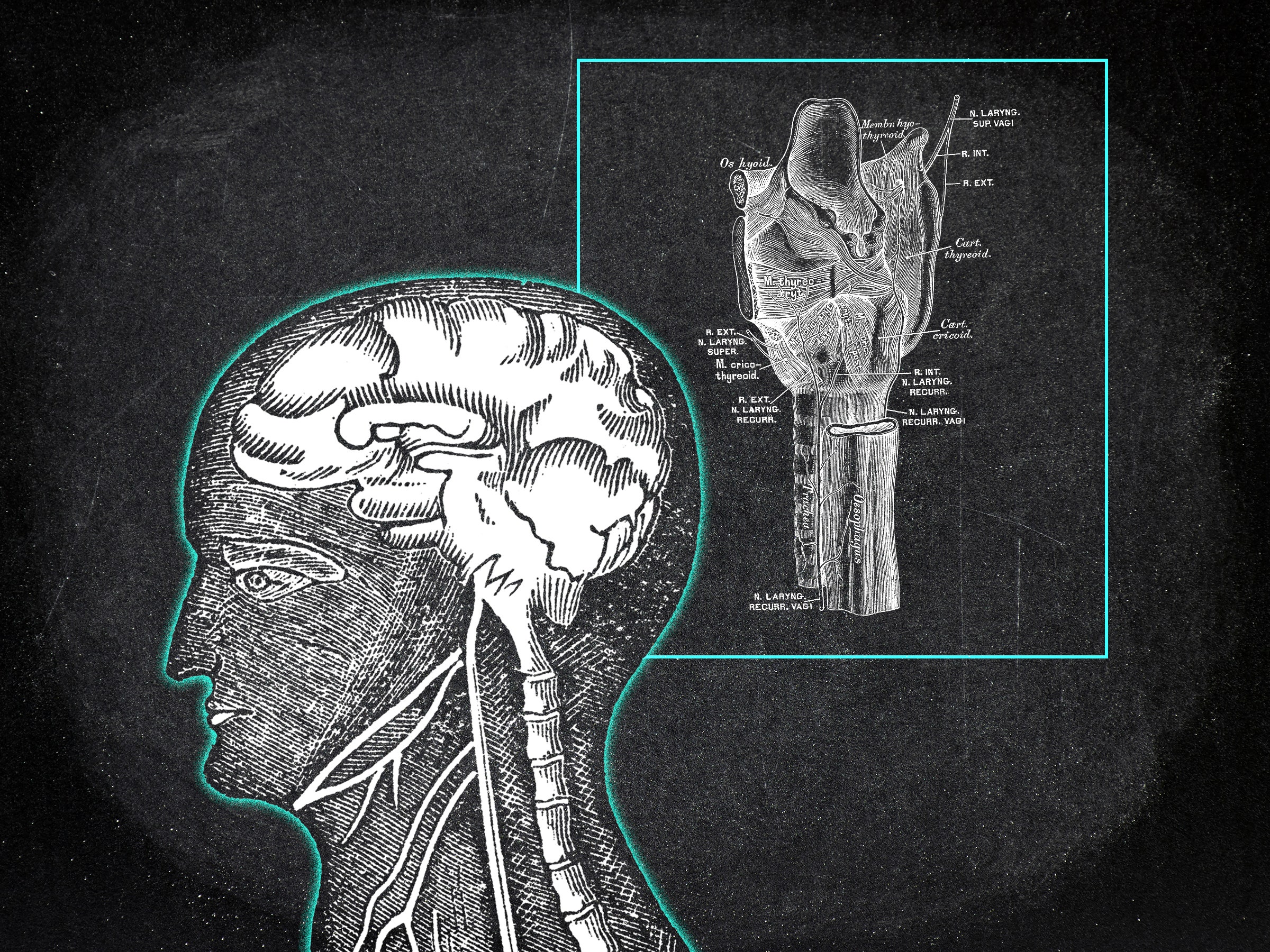
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in the human body, running from the brainstem to the abdomen, touching upon vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
It plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Recent research has shown that the vagus nerve also plays a significant role in the mind-body connection, influencing mood, emotions, and even cognitive functions.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve has been used in treatments for depression, anxiety, and epilepsy, highlighting its importance in mental health.
Furthermore, the vagus nerve is believed to be a key player in the gut-brain axis, influencing communication between the gut and the brain and affecting overall well-being.
Studies have shown that individuals with a stronger vagal tone, or better functioning of the vagus nerve, tend to have better emotional regulation and resilience to stress.
In essence, the vagus nerve is a crucial component in creating the human sense of mind, bridging the gap between physical sensations and emotional experiences.
Understanding the role of the vagus nerve in mental health could lead to innovative treatments for various psychiatric disorders and improve overall well-being.
Overall, the vagus nerve’s influence on the mind-body connection highlights the intricate relationship between our physical and emotional experiences.